15
2025
-
08
What materials are used in gear shaving cutters?
In the field of precision gear manufacturing, gear shaving cutters are essential tools for achieving high-accuracy gear tooth surface finishing. Since these cutters operate under conditions of high strength, heavy wear, and elevated temperatures, selecting the right tool material is crucial.
High-speed steel (HSS) is one of the most widely used base materials for gear shaving cutters, with common grades including M2, M35, and M42. It can maintain a sharp cutting edge at high temperatures and is suitable for long-duration cutting operations. HSS cutters can be reground and reused multiple times.
The hardness of HSS cutters typically ranges from HRC63 to HRC67, with a heat resistance of up to 550–600 °C, making them fully capable of meeting the requirements of gear finishing at moderate cutting speeds (15–25 m/min). Compared to other materials, HSS’s greatest advantage lies in its excellent toughness, allowing it to withstand the intermittent cutting conditions that are inevitable in gear machining, reduce the risk of chipping, and extend tool life.
Tungsten carbide offers extremely high hardness and wear resistance, making it an ideal choice for high-speed and high-precision gear shaving. Carbide gear shaving cutters allow for high cutting speeds and excellent productivity. They also have good heat resistance, enabling stable performance at elevated temperatures. However, their toughness is lower, and they require stable machine tool conditions. Carbide cutters are suitable for machining high-hardness gears, alloy steel gears, and other special gear materials.
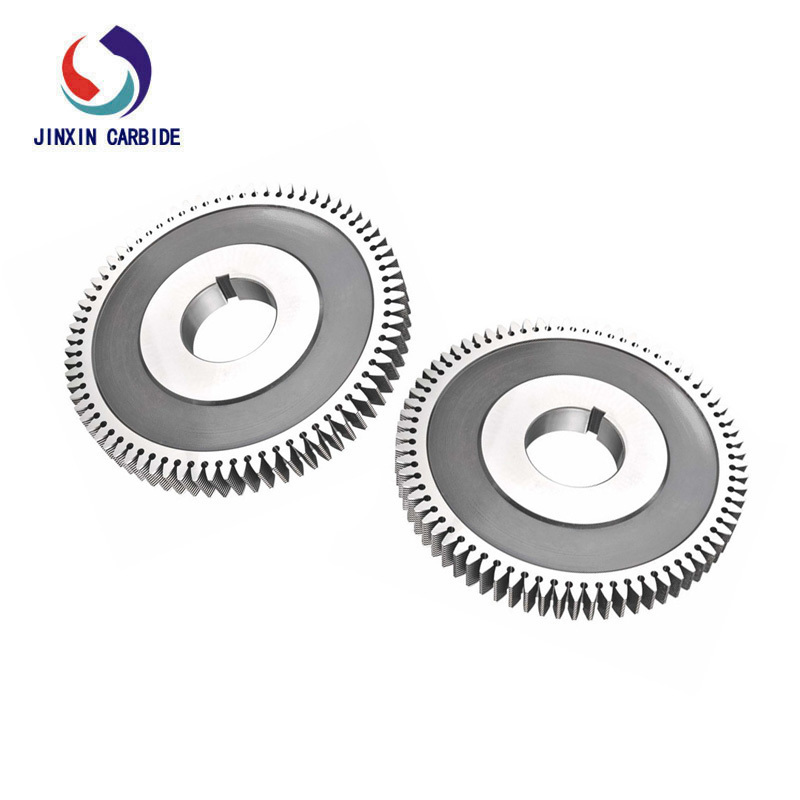

To further enhance cutter performance, HSS or carbide tools are often treated with surface coatings. Using physical vapor deposition (PVD) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technology, a thin film with higher hardness and lower friction coefficient is applied to the tool surface. Common coatings include titanium nitride (TiN), titanium carbonitride (TiCN), and titanium aluminum nitride (TiAlN).
By selecting tool materials based on gear hardness, production volume, and accuracy requirements, you can ensure machining quality while optimizing costs. If you are still unsure about the right cutter material for your specific application, feel free to contact us — we will provide you with customized recommendations!
Related news