05
2025
-
09
what are the most common insert shapes used in od and id turning?
In the field of metal cutting, turning is one of the most widely used machining methods. From simple cylindrical parts to complex internal cavities, turning can efficiently handle a wide range of operations. But when it comes to tool performance, insert shape plays a critical role. So, what are the most common insert shapes for OD (external) and ID (internal) turning? Let’s break it down.
Basic Classification of Turning Insert Shapes
According to ISO standards, the most common insert shapes include C (80° diamond), D (55° diamond), V (35° diamond), T (triangle), and R (round). Each shape offers different cutting strengths and is suited to specific applications.
OD turning: Selection usually focuses on tool tip strength and contour machining capability.
ID turning: The priority is insert stability and the ability to access confined spaces.
Most Common Insert Shapes in OD Turning
1. C Style turning insert (80° Diamond)
C Style inserts are among the most widely used in OD turning.
Strengths: High tool tip strength, versatile, reliable.
Applications: General external turning and facing. These inserts are often considered the “all-purpose” option for roughing and semi-finishing.
2. D Style turning insert (55° Diamond)
Compared with C Style, D Style inserts feature a narrower angle for improved access.
Strengths: Able to reach tighter angles with higher precision.
Applications: Ideal for semi-finishing and finishing, particularly on demanding external profiles and bevels.
3. V Style turning insert (35° Diamond)
V Style inserts are sharp and precise.
Strengths: Excellent for detailed contouring and complex shapes.
Limitations: Lower edge strength, less durable under heavy loads.
Applications: Best for finishing, chamfering, and intricate surface machining.
4. R Style turning insert (Round)
R Style inserts feature a strong, continuous cutting edge.
Strengths: Very robust, smooth cutting, resistant to interruptions.
Applications: Suitable for roughing, heavy cutting, high-feed applications, and interrupted cuts—especially effective when machining castings.
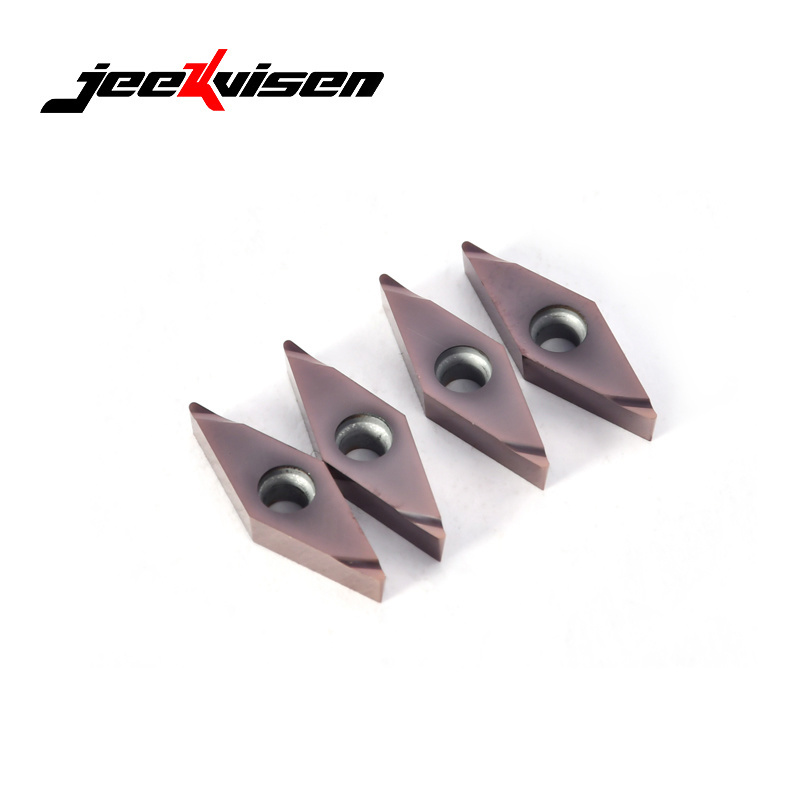

Common Insert Shapes for ID Turning
1. C Style turning insert (80° Diamond)
Strengths: Strong and stable.
Applications: Widely used for most roughing and semi-finishing in internal turning.
2. D Style turning insert (55° Diamond)
Strengths: Narrow approach angle for access to tight spaces.
Applications: Well-suited for small bore machining and high-precision ID finishing.
3. T Style turning insert (Triangle)
Strengths: Three usable cutting edges, cost-effective.
Applications: Common for small- to medium-sized bores where economy and versatility are important.
4. V Style turning insert (35° Diamond)
Strengths: Very sharp, excellent for reaching narrow internal features.
Applications: Complex cavity machining and precision internal chamfering.
Choosing the Right Insert
When selecting inserts for OD or ID turning, shape is only part of the equation. You’ll also need to consider:
Machining requirements: Roughing favors strength and durability, while finishing prioritizes tip geometry and accuracy.
Machine rigidity: If the machine tool lacks rigidity, inserts with a larger tip angle and higher strength will perform better.
Material and application: Workpiece material and cutting conditions also influence the best choice.
By taking these factors into account, you can significantly improve machining efficiency, extend tool life, and achieve better surface quality.
Looking for the best turning insert for your application? Contact us, and we’ll recommend the most suitable solution for your turning needs.
Related news