19
2025
-
09
How to choose the thread turning insert?
Threading plays a critical role in mechanical manufacturing. From automotive components to bolts used in machinery, nearly every precision part requires high-quality threads. Among the various tools available for threading, thread turning inserts are widely regarded as the most effective for achieving both efficiency and precision.
What are thread turning inserts?
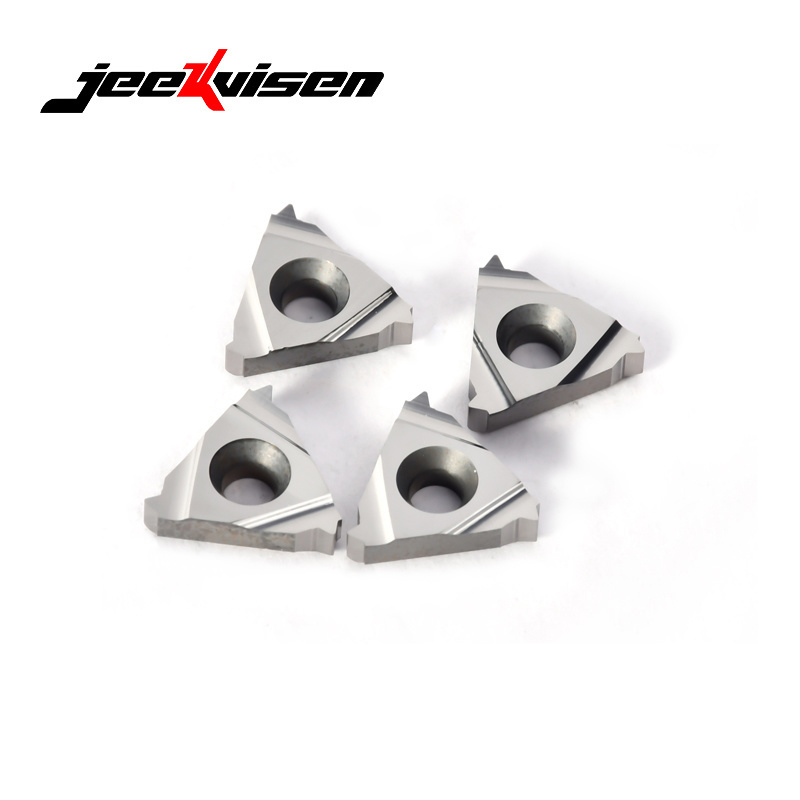
Thread turning inserts are indexable inserts specifically designed for turning internal or external threads. They achieve high-precision threading through the design of the insert geometry and material.
There are three main types of thread turning inserts on the market:
Carbide inserts – the most widely used type, offering high hardness and excellent wear resistance. They are suitable for medium- and high-speed machining.
Ceramic inserts – provide superior high-temperature resistance and are ideal for difficult-to-machine materials such as high-temperature alloys and hardened steels. However, they are more brittle and require machines with higher rigidity.
Coated inserts – not a separate material, but carbide or ceramic inserts with a special surface coating (e.g., TiN or TiAlN). The coating acts as a protective layer, further improving wear resistance and extending tool life.
How to Choose a Thread Turning Insert?
When selecting a thread turning insert, the first factor to consider is the thread type. Common types include metric threads, imperial threads (e.g., 1/2-13 UNC), and pipe threads (e.g., G1/2, NPT1/2, typically used for sealed pipe connections). Single-thread inserts are best for small to medium production volumes, while multi-thread inserts are ideal for continuous, high-speed operations.
Another important factor is the material being machined:
P-type materials (Steel): Includes carbon steel, alloy steel, and high-strength steel. Carbide inserts are recommended due to moderate hardness and good machinability.
M-type materials (Stainless Steel): Stainless steel is sticky and prone to built-up edge, which can affect thread accuracy. It also work-hardens during cutting. Carbide inserts with titanium or tantalum coatings are recommended.
K-type materials (Cast Iron): Brittle and prone to chipping. Carbide inserts with good toughness are preferred.
N-type materials (Non-ferrous metals): Includes aluminum, copper, and magnesium alloys. These materials are soft, sticky, and prone to scratching. High-speed steel inserts or uncoated, ultra-fine-grain carbide inserts are suitable.
Selecting the right thread turning insert can significantly improve machining efficiency, extend tool life, and ensure thread accuracy. Contact Jinxin and we can assist you with thread turning insert selection and provide you with the optimal solution.
Related news