26
2025
-
09
What is the difference between cermet inserts and carbide inserts?
With the continuous advancement of materials technology, cermet and carbide inserts have become the two most common types of cutting tools used in industrial production. Besides their distinct material differences, they each possess advantages and disadvantages in production and processing.
Cermet inserts are a composite material of metal and ceramic, primarily composed of titanium carbide (TiC), titanium nitride (TiN), and titanium carbonitride (TiCN), combined with metals such as nickel, cobalt, and molybdenum.
Features of Cermet Inserts
High Hardness and Wear Resistance: Cermet inserts offer higher hardness and wear resistance than conventional carbide, maintaining a sharp edge even during extended cutting cycles and extending tool life.
Excellent Heat Resistance: They offer excellent high-temperature performance, making them suitable for high-speed and dry cutting, maintaining stable cutting performance even in high-temperature environments.
Applications: Ideal for continuous cutting, finishing, and machining hardened steel, achieving a high surface finish and often used in processes requiring stringent workpiece quality.
Disadvantages: They lack toughness and impact resistance, making them unsuitable for interrupted cutting and deep cutting. They are also slightly more expensive than conventional carbide inserts.
Carbide inserts are typically made primarily of tungsten carbide (WC), with metal binders such as cobalt (Co) and nickel (Ni). This combination maintains high hardness while maintaining a certain degree of toughness, making them widely used in industrial production.
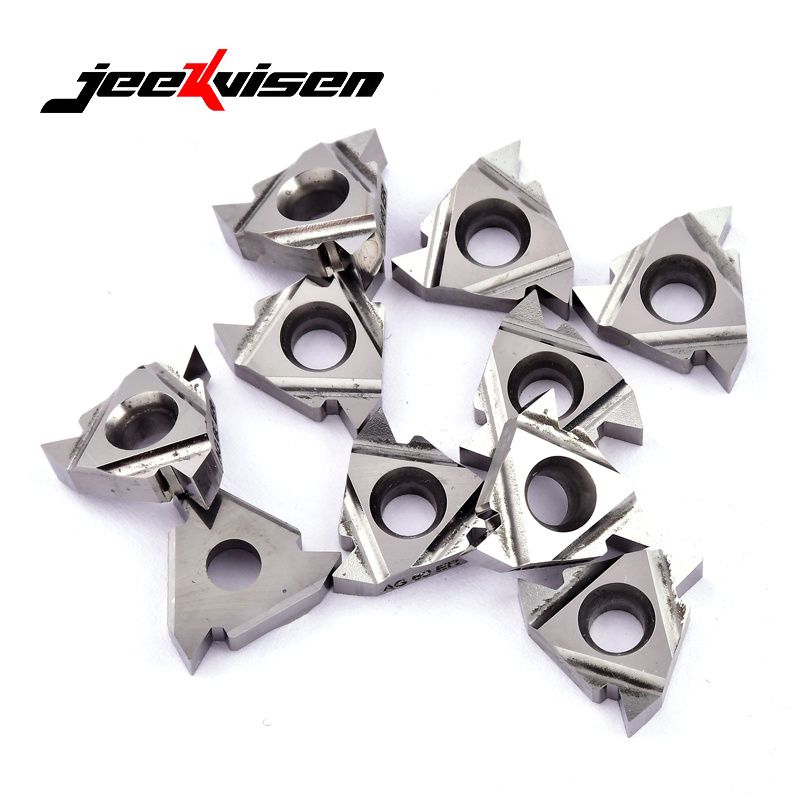

Carbide Insert Features
Balanced Hardness and Toughness: Compared to ceramic inserts, they offer greater impact resistance and adaptability.
Wide Cutting Range: They can be reliably used on steel, stainless steel, non-ferrous metals, and common everyday machining.
Applications: Particularly suitable for medium- and low-speed cutting, as well as machining tasks requiring versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Disadvantages: They lack the heat resistance and high-speed performance of ceramic inserts.
It's easy to see that cermet inserts are more suitable for high-speed cutting and finishing operations requiring high surface quality, while also offering excellent high-temperature resistance. Carbide inserts, on the other hand, offer a wider range of applications, combining both hardness and toughness. The final choice should be determined based on the material being machined, cutting speed, and production cost.
If you are looking for high-quality cermet or carbide inserts, please contact Jinxin for the solution that best suits your needs.
Related news